
Central banks of many countries are considering creating a digital version of their existing fiat currency after watching the increasing popularity and demand for cryptocurrencies, such as Ethereum and Bitcoin. The digital version of a fiat currency is known as Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC).
So, what is CBDC? What will be the possible advantages and disadvantages or threats of having a central and controlled digital currency?
Overview of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDC)
The digital or electronic form of fiat currency/cash issued by the central bank of a country is CBDC or Central Bank Digital Currency. For example, the digital version of the Chinese Yuan, which has been named ‘e-CNY’. A CBDC would qualify as a ‘legal tender’ and can be used for making transactions. If the global adoption rate of CBDC increases, it could possibly replace paper money in the coming years.
In the last few years, the world has become drastically digital. There has been a significant increase in the adoption of digital payments, financial technology, and cryptocurrency. In fact, the acceptance of cryptocurrencies as a form of investment asset, and as well as a form of instant payment has made many countries’ governments divert their attention towards CBDCs.
According to a 2021 BIS survey, 86% of the global central banks are researching the potential of their own digital currency or CBDC, of which 14% are already in the process of running their pilot programs.
The Advantages of Having A Central Bank Issued Digital Currency
CBDCs can help central banks of many countries increase financial inclusion. Thus, allowing banked and unbanked citizens to create accounts and hold funds at a central bank. This will also provide greater financial inclusion to the unbanked and underbanked. Having a digital central currency will also help bring in more transparency amongst private companies when they carry out transactions in local currencies as digital transactions are traceable compared to cash. This would also help prevent illicit activities since the payments made would need to be done using the digital form of currencies making it transparent, traceable, and immutable.
Unfortunately, there is a downside to having CBDCs as well.
Having central banks issue digital currencies (CBDCs) could result in increased control of central banks, and government authorities. Secondly, financial regulators could lose control over the supply of money since consumers would prefer CBDCs over cash considering that individuals and businesses are increasingly adopting digital forms of transactions and buying cryptocurrencies, such as Bitcoin.
Furthermore, if individuals are able to have digital wallets with the Central bank itself and hold CBDCs, banks could lose their control on economic stability and money in general. This could also make private banks obsolete resulting in more control of the government over the financial situation of a country.
If a central body ends up having more control over the digital currency, and access to the financial transactions record of consumers, it defeats the sole purpose of inventing a digital currency which is to build an open, decentralized financial system wherein individuals and businesses are more in control of their finances.
Types of Central Bank Digital Currency (CBDCs)
Wholesale CBDC
Wholesale CBDC could be considered as ‘central bank reserves’ that exist currently for paper money. They will be useful in the settlement of interbank transfers and wholesale transactions, such as the settlement payments between financial institutions. Wholesale CBDCs could potentially improve efficiency and risk management in settlement.
Retail CBDC
Unlike wholesale CBDCs, retail CBDCs will be available to individual and business consumers. They can use it like traditional fiat currency (cash). Individuals and businesses will be able to make payments using retail CBDCs for dining, shopping, paying utility bills, and other similar expenses. While, businesses may use it to make instant payments to their suppliers, and other vendors.
CBDC Structure
Token
A token-based CBDC structure exists for retail CBDC. Consumers can use the token form to pay for normal expenses. A token would be like a digital coin version of monetary bills.
Account
An account-based CBDC structure exists for wholesale CBDCs since reserve accounts’ balances and most forms of commercial bank money are account-based.
CBDC Technology
This is the underlying technology behind CBDC. As of now, many central bank technology partners are relying on Distributed ledger technology (DLT) while some are working on non-DLT based technology.
DLT
In the ‘Distributed Ledger Technology’ (DLT) a digital system is used for recording the transaction of assets. Detailed information related to a transaction is recorded in multiple places at any given time to prevent tampering, and loss of information. DLT work on blockchain technology. Trials with DLT are currently being executed by central banks and their respective technology partners mainly for wholesale CBDCs.
Non-DLT
CBDCs, where the underlying technology is not blockchain-based, is called non-DLT. Central banks of various countries and their partners are conducting trials using non-DLT for retail CBDCs.
Programmability
CBDCs may or may not be programmable. CBDCs that are programmable can be useful in making automated payments on an ongoing basis after they meet certain qualifying conditions. Thus, with programmable CBDC payments can be automated based on predetermined logic.
Interoperability
A CBDC may or may not be interoperable depending on the decision of the central bank of a country. Interoperability includes the incorporation of any characteristic of systems that enables payment systems to exchange information. With the help of this characteristic, a CBDC could achieve an easy flow of funds to and from other payments system. Thus, ensuring the coexistence of a CBDC system within a wider payment ecosystem.
Central Bank Digital Currencies (CBDCs) Status in Various Countries
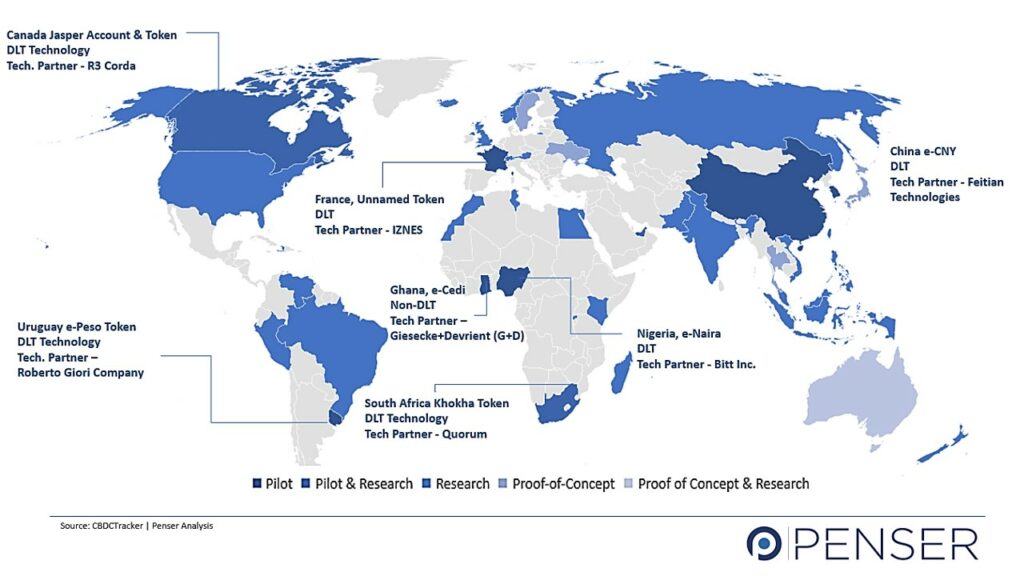
Learn more about the current status of CBDCs in various countries
Having said that, CBDCs are growing more realistic and feasible with each passing day. Even though the concept of CBDC is in a nascent stage, as with any other cryptocurrency, it has more than one side.
About Penser
As an expert in fintech consulting and payments consulting, Penser tracks new trends in the industry. We offer due diligence services for investors and vendors as well as digital transformation and strategic planning services. Get in touch with us at hello@penser.co.uk to know more about how we can help your business.
