
‘Buy Now Pay Later’ is currently the most popular form of digital payment. The economic downturn brought in by the global pandemic being one of the critical reasons for its growth. Splitit, a BNPL supporting fintech (financial technology) company, saw a 206% YOY growth in merchant sales processed by them. While Afterpay, an Australian BNPL fintech company, saw a 219% increase in its U.S. customer base.
According to Business Insider, the BNPL industry could reach US$680 billion in transaction volume worldwide by 2025.
However, with every country’s economy currently facing turmoil, one wonders if ‘Buy Now Pay Later’ (BNPL) is really feasible from a long-term perspective.
What is Buy Now, Pay Later (BNPL)?
Buy Now Pay Later (BNPL) allows consumers to shop on e-commerce platforms or physical stores and pay for their purchases later. Consumers can repay either as a lump sum amount or in monthly instalments.
Fintech companies, who provide this offer to consumers, do so based on the consumer’s credit history and payment behaviour.
In some ways, it is similar to purchasing via credit card, except that in the case of BNPL no physical card is necessary to avail the pay later option.
How Does BNPL Work?
BNPL service providers and merchants mutually agree upon a fee percentage that the merchant will pay for each BNPL associated sale. The fee percentage usually ranges from 2%t to 8% of the purchase amount. The BNPL payment service platform is then integrated into the merchant’s website at the point of sale (POS).
Consumers can choose their preferred BNPL service provider (if multiple service providers’ platforms are available. They will need to fill in their details and choose a preferred payment plan. The BNPL service provider will then conduct a real-time credit check. Upon approval, the provider will display to the customer the terms of service — the repayment schedule. From there, customers can check out as usual.
BNPL Industry Overview
Although not entirely a new concept, the ‘Buy Now Pay Later’ (BNPL) industry resurged during the pandemic. The global economic fallout leading to the limited purchasing power of consumers, coupled with attractive zero interest, easy-pay, and other benefits by fintech companies being the major reasons for this resurgence.
In Europe and U.K., BNPL usage is expected to increase in the coming years.
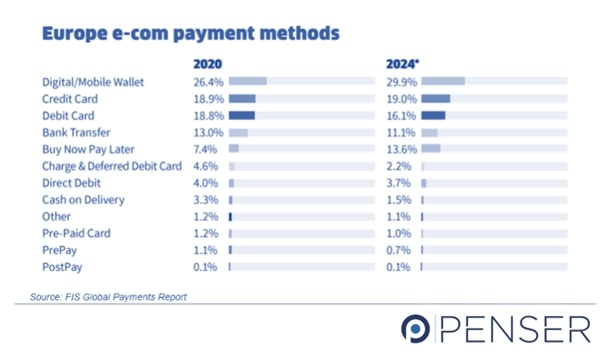
As per a research conducted by Equifax, consumer general-purpose credit card balances fell by 11 percent, from $818 billion on March 2, 2020, to $727 billion on July 27, 2020 (COVID-19 emergency period).
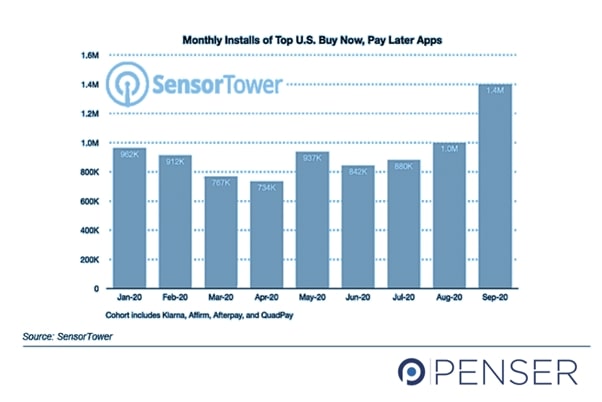
In the U.S. alone, BNPL applications were downloaded by 1.4 million people in 2020.
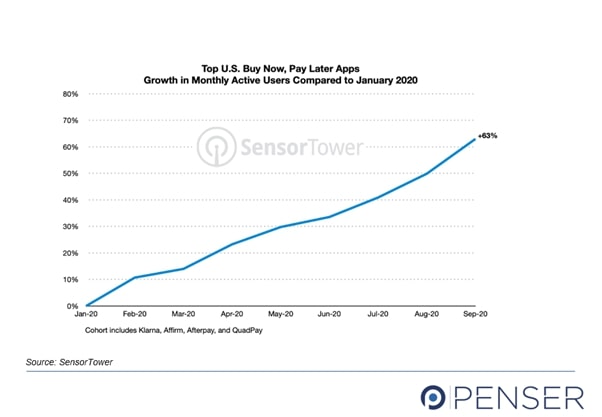
The monthly active users in the U.S rose by 63% between January 2020 to September 2020.
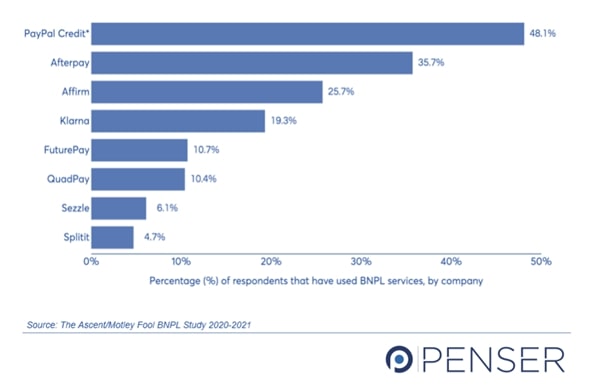
According to ‘The Ascent’s March 2021 survey’ of U.S. consumers:
- 8% of U.S.-based consumers have used a buy now, pay later service.
- Age plays no role. 62% growth in use was seen amongst users in the 18-24 age group, while a 98% growth was seen in users above 55 years of age.
- 41% of these individuals did not want to liquidate their existing cash reserve on a purchase, while 25% stated temporary unemployment as their reason.
Coherent Market Insights analysis shows the global ‘Buy Now Pay Later’ platforms market to surpass US$ 33,638.3 mn. by 2027, registering a CAGR of 21.2% between 2019 to 2027.
Fintech Companies Offering BNPL
The increasing popularity of BNPL coupled with possible growth opportunities has attracted many fintech companies to enter the BNPL market.

BNPL providers fall into three categories:
Direct Providers, such as Klarna, Afterpay, Affirm. Direct BNPL service providers offer BNPL products at the point-of-sale (POS) on a merchant’s website. The financial risk is borne entirely by these companies.
Facilitators, such as Mastercard, and Stripe. Facilitator companies partner with merchants enabling them to directly provide buy now pay later service to their consumers.
Retroactive Providers, such as Chase and American Express. Consumers use their credit cards for the purchase, and avail flexible payment options while making the credit card payment.
Key BNPL Market Dominating Companies
Advantages of Buy Now, Pay Later
There is no denying that BNPL is beneficial for consumers, merchants, and fintech companies alike.
From a consumer’s viewpoint:
- Unlike credit cards, BNPL comes with no interest expense. Although companies may levy late payment fees on delayed payments.
- BNPL enables consumers to make expensive purchases, such as: electronics, furniture, or other high-end products without worrying about funding.
- BNPL purchases can be made without credit cards or taking a loan.
- An individual can simply connect with Afterpay, PayPal, or any other fintech that offers BNPL, and avail instant credit. A one-time-password (OTP) helps process payments on online platforms. While for physical stores, the individual can scan the QR-code.
For merchants, it means:
- More buyers, repeat customers, and bigger transaction amounts. BNPL enables consumers to finally make those big purchases they have been putting off. This enables higher conversion rates for merchants
- Merchants receive the full payment upfront from the fintech companies after deducting their percentage share of 2% to 8%. They do not have to worry about the financial risk. Thus, making BNPL a no-risk offer for them.
For the fintech proving BNPL:
- The fintech receives a certain percentage of the sales revenue from the merchant.
- They also receive interest and other fee income, late payment fee.
However, they shoulder the maximum risk (of non-payment by the consumer) associated with every transaction.
BNPL Risks for Fintech Companies
Due to the ongoing social restrictions and global economic conditions, individuals and small business owners are facing financial crisis. Digital lending, thus, becomes critical and should be encouraged.
Digital lending provides easy access to capital for individuals and businesses in need. Unlike traditional banking system, fintech companies associated with digital lending ensure a simple streamlined process to avail loans without much hassle.
However, the associated merchant and consumer risks cannot be ignored. Companies need to streamline their loan underwriting process and incorporate a feasible recovery mechanism. Significant efforts need to be put into finalizing borrowers and building a credit discipline.
Fintech companies also need to consider the ‘loan stacking’ issue, which may happen when an individual avails multiple loans through several companies within a duration of 36-48 hours. The loans may simultaneously be approved resulting in a loan beyond one’s credit limit. As BNPL platforms and users increase, such fraud practices are also likely to increase.
Mitigating BNPL Risks
Some ways in which fintech companies can mitigate the risks associated with BNPL are:
- Verifying the consumers’ income level along with credit history to ensure that the monthly payment amount does not cross 10% to 15% of their after-tax income.
- Charging a BNPL application or processing fee to ensure genuine consumers.
- Opting for direct debit, or direct transfer from the consumer’s bank account for repayments to avoid defaults.
- BNPL service providers should hold an industry-standard credit license.
- Regulating BNPL purchases above a certain amount. For example, BNPL facility on purchases above £1000 should not be provided without significant affordability checks. Additionally, the existing debt data (credit card loan, mortgage, etc.) of the consumer should be available to BNPL service providers and properly reviewed before approving the loan.
Conclusion
BNPL transactions are projected to reach close to US$ 680 billion worldwide by 2025, making it the fastest-growing form of digital payments. The ability to buy now and pay later encourages sales which normally would not happen. However, the risks of default cannot be ignored.
UK FCA’s BNPL Risk Mitigating Measures
Recently, in the U.K., where the unregulated BNPL market more than trebled in size in 2020, FCA’s Board’s former interim chief executive Chris Woolard recommends immediate changes to bring all BNPL products within the FCA’s regulatory. U.K. FCA will authorize and regulate BNPL lenders upon legislation. This regulation will require lenders to address affordability assessments and treatment of consumers in financial difficulty. BNPL advertisement will be brought within the financial promotions’ regime, requiring them to give sufficient and clear information about the product without being misleading.
Australian ASIC’s BNPL Risk Mitigating Measures
In Australia, an Australian Securities and Investments Commission (ASIC) survey revealed that 20% of consumers had to cut back on or went without essentials (such as meals) to make BNPL payments. While 15% of surveyed consumers had to take out an additional loan.
The ‘no interest’ promotion method of BNPL companies has lured several consumers into spending beyond their means. Thus, ringing the alarm bell for change.
Therefore, from October 2021, design and distribution obligations (DDO) will apply to BNPL arrangements like most products regulated by ASIC. BNPL providers will need to access industry knowledge, information about their users, and other data to define the target market. BNPL providers must review and monitor their arrangements with merchants and consumers. How companies are selling BNPL services, and to whom? For example, if a BNPL provider markets its BNPL service arrangement as cost-free or low-cost access to deferred payment, this should be the main consideration in terms of their DDO. If these schemes are, however, negatively impacting consumers, the BNPL provider needs to audit and rectify the situation.
The Australian Finance Industry Association furth announced that it is developing an industry code of practice for BNPL providers (BNPL Code). This BNPL Code can play an important part in delivering benefits to both consumers and merchants and rebuilding confidence in the Australian BNPL industry.
Financial regulatory authorities in other countries should take similar regulatory measures to prevent the lucrative ‘Buy Now Pay Later’ industry from turning into a global economic problem.
Penser is a specialist fintech and payments consulting firm with experience working for clients in the digital payments, card payments, and mobile payments sectors. We offer digital transformation, due diligence, and strategic planning services.
Contact us to find out how we can help boost your business.
